Discover how Ferinject could help your patients with non‑dialysis chronic kidney disease
 |
Ferinject is indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency when: oral iron preparations are ineffective; oral iron |
How could Ferinject® (ferric carboxymaltose) help your patients
with non-dialysis chronic kidney disease?
Anaemia is a common complication in non-dialysis chronic
kidney disease (ND-CKD)2
- Anaemia affects 3 out of 4 patients with ND-CKD and GFR <152
- Prevalence of anaemia increases with progression of ND-CKD2
- Anaemia has a physical and emotional impact on patients with ND-CKD3-5
- Studies suggest that 60-70% of non-dialysis patients with CKD (stage 3-5) may be iron deficient6
Iron is a cornerstone of treatment for iron deficiency anaemia in patients with
ND-CKD
In anaemia of CKD, iron sequestration, plus the rapid demands of the bone marrow, means that additional
iron therapy is often needed to support the use of ESAs:7
|
Functional iron deficiency or iron restricted erythropoiesis |
+/- ESA |
Efficient production of red blood cells |
Sustainable correction of anaemia in ND-CKD |
Sustainable correction of iron deficiency anaemia with Ferinject:
results from the FIND-CKD study8
In the 56-week, open label, randomised FIND-CKD study that compared efficacy and safety of IV Ferinject, targeted to different
ferritin levels, with daily oral ferrous sulphate therapy:
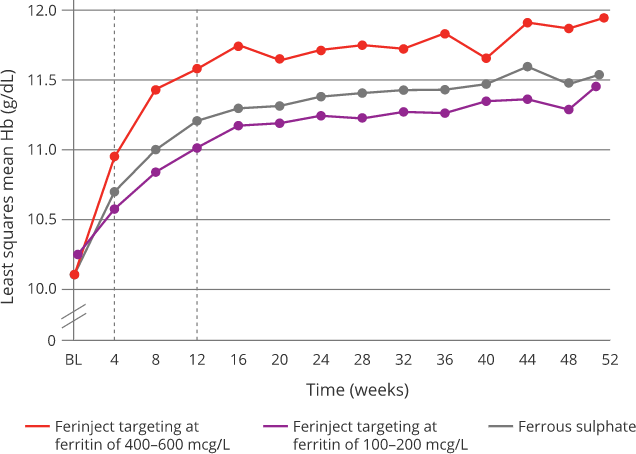
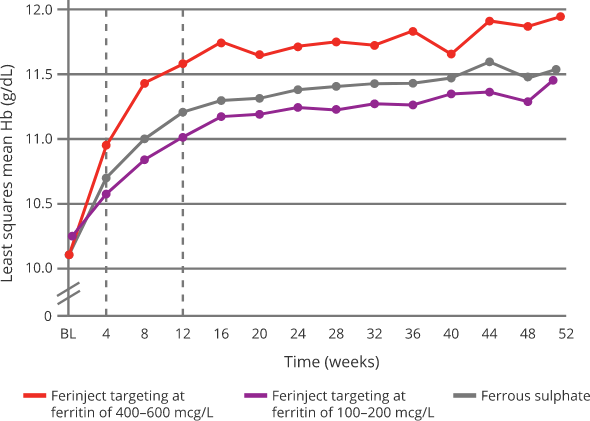
- Targeting higher ferritin levels with Ferinject allowed a quick and sustainable correction of iron deficiency anaemia compared with targeting
low-ferritin with Ferinject or oral ferrous sulphate8
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on ferritin8
|
|
Targeting 400-600 mcg/L serum ferritin with Ferinject:8
|
Oral ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin > 200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin < 100 mcg/L
|
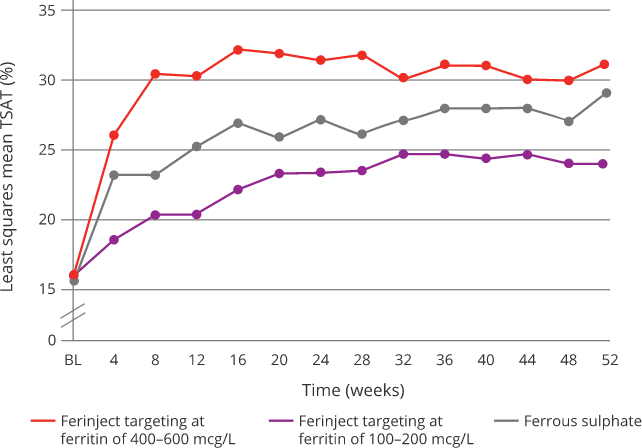
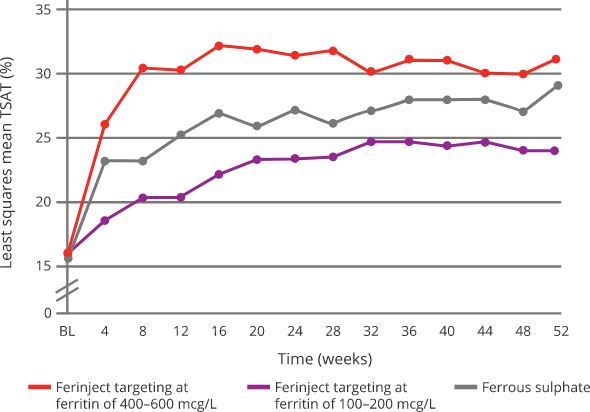
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on TSAT8
|
|
Targeting 400-600 mcg/L serum ferritin with Ferinject:8
|
Oral ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin > 200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin < 100 mcg/L
|
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on Hb8
|
|
Targeting 400-600 mcg/L serum ferritin with Ferinject:8
|
Oral ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin > 200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin < 100 mcg/L
|
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on ferritin8
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on ferritin8
|
|
Targeting 400-600 mcg/L serum ferritin with Ferinject:8
|
Oral ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin > 200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin < 100 mcg/L
|
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on TSAT8
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on TSAT8
|
|
Targeting 400-600 mcg/L serum ferritin with Ferinject:8
|
Oral ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin > 200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin < 100 mcg/L
|
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on Hb8
Effect of Ferinject versus ferrous sulphate on Hb8
|
|
Targeting 400-600 mcg/L serum ferritin with Ferinject:8
|
Oral ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin > 200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin < 100 mcg/L
|
Ferinject has a well-characterised tolerability profile:1
- The most commonly reported adverse drug reaction (ADR) is nausea (3.2%), followed by injection/infusion site reactions, hypophosphataemia, headache, flushing, dizziness and hypertension. Injection/infusion site reactions comprise several ADRs which individually are either uncommon or rare
- The most serious ADR is anaphylactic reactions (rare); fatalities have been reported. Ferinject has a documented frequency of serious hypersensitivity reactions of less than 1 in 1,000. There have been reports of hypersensitivity reactions which progressed to Kounis syndrome (acute allergic coronary arteriospasm that can result in myocardial infarction)
- Ferinject should only be administered when staff trained to evaluate and manage anaphylactic reactions is immediately available, in an environment where full resuscitation facilities can be assured. The patient should be observed for adverse effects for at least 30 minutes following each Ferinject administration
- If hypersensitivity reactions or signs of intolerance occur during administration, the treatment must be stopped immediately. Facilities for cardio respiratory resuscitation and equipment for handling acute anaphylactic reactions should be available, including an injectable 1:1,000 adrenaline solution
- Hypophosphataemia is a common (≥1/100 to <1/10) adverse drug reaction. Symptomatic hypophosphataemia leading to osteomalacia and fractures requiring clinical intervention including surgery has been reported in the post marketing setting. Patients should be asked to seek medical advice if they experience worsening fatigue with myalgias or bone pain. Serum phosphate should be monitored in patients who receive multiple administrations at higher doses or long-term treatment, and those with existing risk factors for hypophosphataemia. In case of persisting hypophosphataemia, treatment with ferric carboxymaltose should be re-evaluated
Please refer to the Ferinject Summary of Product Characteristics for complete tolerability information
Find out moreFIND-CKD study design:8
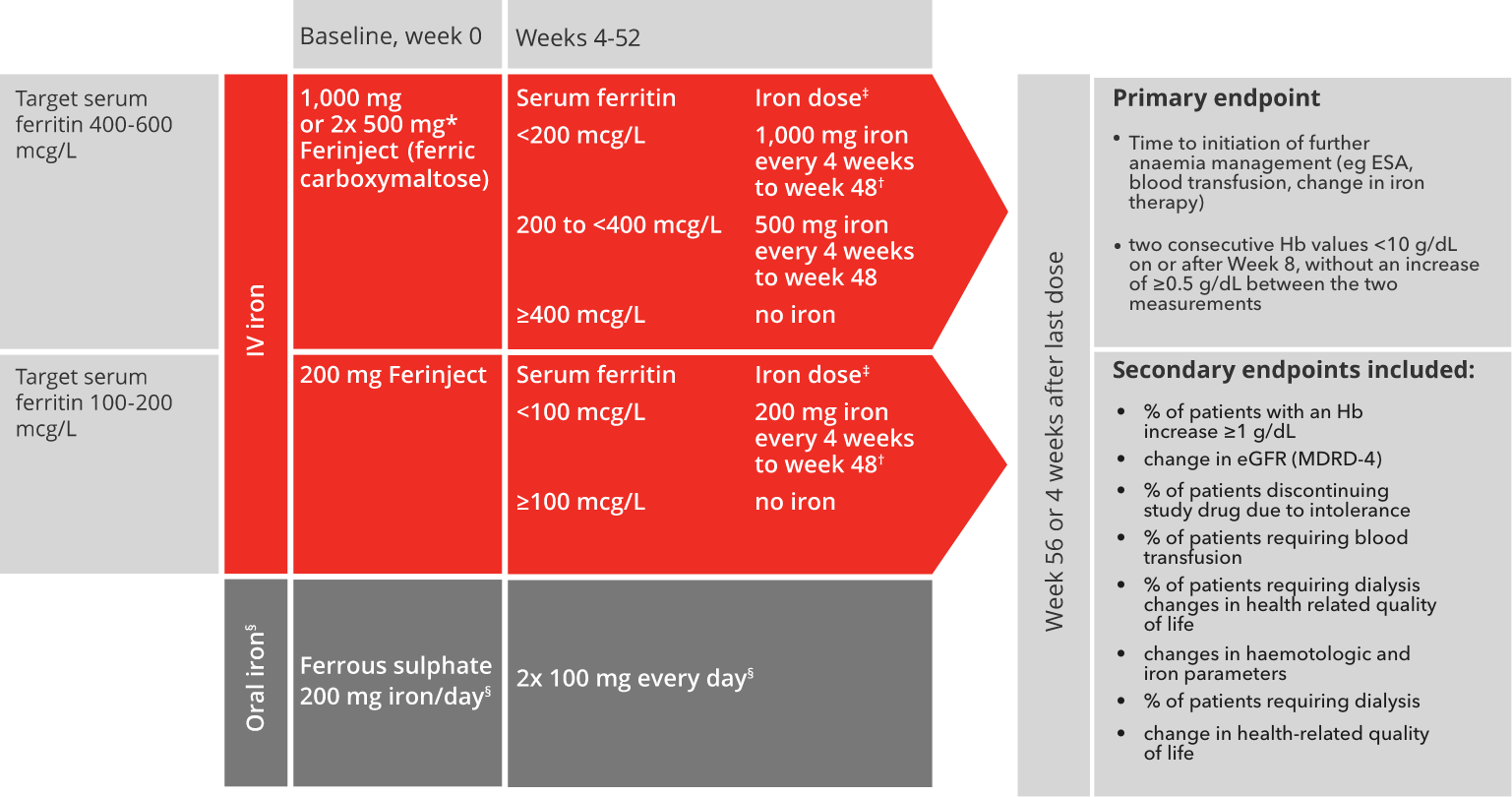
Adapted from Macdougall I C et al, 2014.8
*Patients ≤66 kg: 500 mg iron on days 0 and 7.8
†Patients ≤66 kg: 500 mg iron on day of visit and 500 mg iron one week later.8
‡No administration if transferrin saturation level ≥40%.8
§Ferrous sulphate was withheld if serum ferritin >200 mcg/L and restarted if/when serum ferritin <100 mcg/L.
The last dose of Ferinject was administered at week 48, and the last dose of ferrous sulphate was administered at week 52.8
eGFR, estimated glomerular filtration rate; ESA, erythropoiesis stimulating agent; Hb, haemoglobin; IV, intravenous; MDRD, Modification of Diet in Renal Disease.
8. Macdougall IC et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014;29:2075–2084.
ADR, adverse drug reaction; CKD, chronic kidney disease; CI, confidence interval; ERBP, European Renal Best Practice; ESA, erythropoiesis stimulating agent; Hb, haemoglobin; HR, hazard ratio; GFR, glomerular filtration rate; ID, Iron deficiency; IV, intravenous; KDIGO, Kidney Disease Improving Global Outcomes; ND-CKD, non-dialysis chronic kidney disease; NICE, National Institute for Health and Care Excellence; TSAT, transferrin saturation.
1. Ferinject Summary of Product Characteristics. 2. McClellan W, et al. Curr Med Res Opin 2004;20(9):1501–10. 3. Mehdi U, et al. Diabetes Care 2009;32(7):1320–26. 4. Agarwal R. Am J Nephrol 2007;27(6):565–71. 5. Eriksson D, et al. BMC Nephrol 2016;17(1):97. 6. Fishbane S et al. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2009;4:57–61. 7. Macdougall IC. Curr Med Res Opin 2010;26(2):473–82. 8. Macdougall IC, et al. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2014;29(11):2075-84.
Ferinject in patients with heart failure
Oral or IV iron
Welcome to